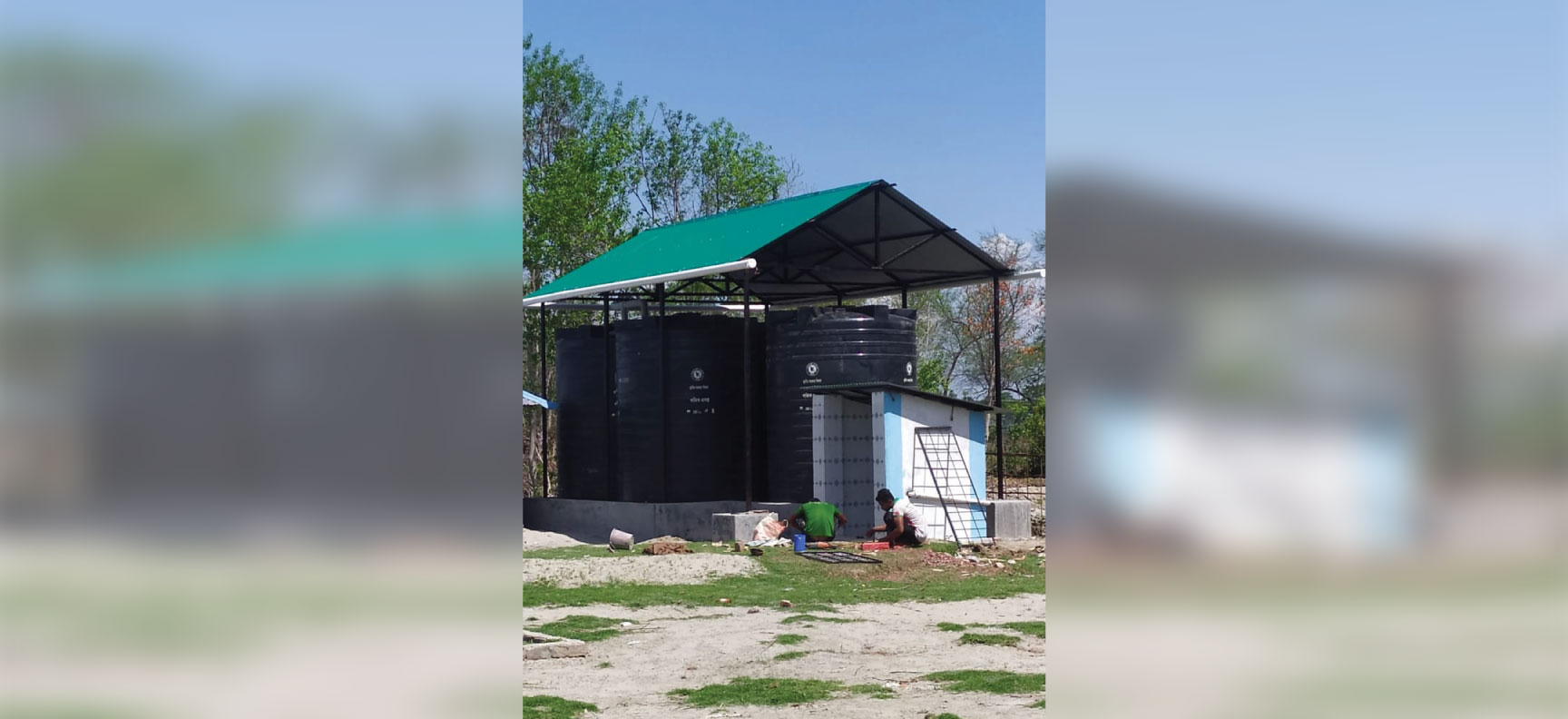
Rainwater harvesting is one of the feasible fresh water sources in Bangladesh’s coastal areas. Recently, numerous programs and initiatives have been implemented to promote and install rainwater harvesting systems in Bangladesh’s coastal and arsenic-affected areas. Additionally, the country receives a lot of rain each year. Bangladesh receives approximately 2200 millimeters of precipitation annually, with 75% of it falling between May and September.
Rainwater harvested by the Dhaka Water Supply and Sewerage Authority (WASA) has been shown to be arsenic-free and to be a suitable and acceptable source of potable water due to its physical, chemical, and bacteriological characteristics. Rainwater can be used for non-potable purposes like flushing toilets, watering gardens, and floor washing at the household level in urban areas. It becomes the primary source of potable water for drinking, bathing, and cooking in rural areas.
Bangladesh’s water resources management faces significant challenges in resolving a wide range of issues. Arsenic contamination, salinity, and the ever-increasing water requirements of a population and economy growing at an ever-increasing rate are the most pressing of these.
As per a concentrate by the Institute of Water Modelling in Bangladesh’s capital city, its groundwater level is falling by three meters each year. Populace has expanded and industry has extended, stream water has become tainted with modern waste. Today, groundwater is supposed to fulfill more than 80% of the city’s water supply. Around 150bn liters of water could be collected during the storm season in Dhaka city alone.
Water collecting is subsequently a possible choice of water supply to the beach front and arsenic impacted provincial networks in Bangladesh. Water gathering, minimal expense frameworks that gather and store water for all year use, offers a financially savvy and reasonable answer for ease water emergency.
In a new workshop, global NGO Water Aid<> and The Institute of Engineers, Bangladesh reasoned that water reaping should be remembered for laying out the nation’s local laws. Consequently, In the new years from 2000-2004, a great deal of projects and tremendous speculations have been finished by government association and NGOs with the monetary help from global giver organizations to advance and introduce a few kinds of family and local area based water gathering frameworks both in the beach front and arsenic impacted regions in Bangladesh as an elective water supply sources other than groundwater. Beginning around 1997, around 1000 water reaping frameworks have been introduced in the country, fundamentally in rustic regions (UNDP).

Bangladesh’s water resources management faces significant challenges in resolving a wide range of issues. Arsenic contamination, salinity, and the ever-increasing water requirements of a population and economy growing at an ever-increasing rate are the most pressing of these.
As per a concentrate by the Institute of Water Modelling in Bangladesh’s capital city, its groundwater level is falling by three meters each year. Populace has expanded and industry has extended, stream water has become tainted with modern waste. Today, groundwater is supposed to fulfill more than 80% of the city’s water supply. Around 150bn liters of water could be collected during the storm season in Dhaka city alone.
Water collecting is subsequently a possible choice of water supply to the beach front and arsenic impacted provincial networks in Bangladesh. Water gathering, minimal expense frameworks that gather and store water for all year use, offers a financially savvy and reasonable answer for ease water emergency.
In a new workshop, global NGO Water Aid<> and The Institute of Engineers, Bangladesh reasoned that water reaping should be remembered for laying out the nation’s local laws. Consequently, In the new years from 2000-2004, a great deal of projects and tremendous speculations have been finished by government association and NGOs with the monetary help from global giver organizations to advance and introduce a few kinds of family and local area based water gathering frameworks both in the beach front and arsenic impacted regions in Bangladesh as an elective water supply sources other than groundwater. Beginning around 1997, around 1000 water reaping frameworks have been introduced in the country, fundamentally in rustic regions (UNDP).
Conditions Favouring Rainwater Harvesting
Water reaping as a choice can be embraced to work with accessibility of protected and reasonable drinking water supplies and to safeguard normal melancholies and water bodies in major metropolitan regions for re-energize of underground springs.
Arsenic Contamination
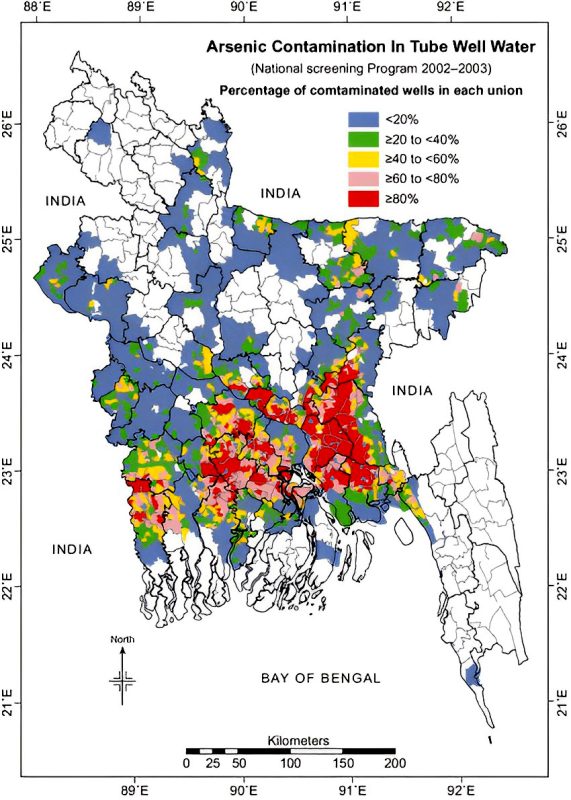
Arsenic tainting of ground water influences numerous country regions, while a few metropolitan regions including the capital, Dhaka City, need adequate consumable ground water to satisfy the need. Accordingly, populace vigorously reliant upon hand siphons and cylinder wells are presented to arsenic related serious wellbeing risk. World Health Organization depicted the arsenic tainting in Bangladesh as “the biggest mass harming of a populace ever”.
Water reaping is being viewed as one of the significant substitute innovation with comparable advantages and comfort to supplant these hand siphons and cylinder wells.
Salinity
Bangladesh has extremely lengthy shorelines and beach front region covers 20,000 square km region. In the beach front regions, spring conditions are not reasonable for shallow cylinder well and high saltiness in both surface and groundwater are the primary requirements for the improvement of a reliable water supply framework. Customary water gathering for the purpose of savoring a restricted scale has been the normal practice for long time and in certain region of the beach front locale with high saltiness issue. Around 36% families have been found to rehearse water gathering in the stormy season for drinking reason and homegrown necessities.
Fluoride Concentration
As of late there has been some worry about fluoride in savoring water Bangladesh. In a few country areas of Bangladesh, the fluoride focus in water is accounted for higher than greatest passable breaking point (MPL). In country regions, where the drinking water is drawn from accessible sources, for example, tube wells, hand siphons or lakes, in which the fluoride focus might surpass the MPL. To moderate the fluoride fixation, it is crucial for treat the overabundance fluoride concentrated water sources or to stay away from the fluoride concentrated water. The evasion of fluoride is likewise probable by the utilization of water, one of the most flawless types of water with practically no fluoride. There are number of benefits for considering water gathering as a substitute technique.
Arsenic Contamination Report 2002-2003
Source: https://www.researchgate.net/
